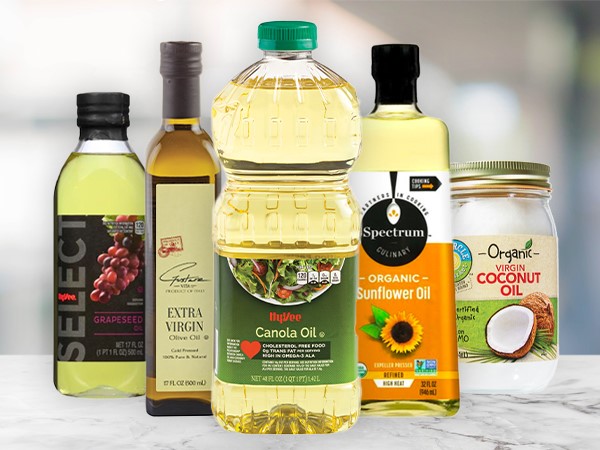
Description
Oils perform a variety of functions in cooking, but they are not interchangeable. While all are classified as fats, they perform differently in how they enhance the flavors of food depending on the cooking method. Some can withstand high levels of heat before smoking (the smoke point) and are great for frying or sauteing. Others perform best at low or no heat as the base for salad dressings. Here's an easy guide on how to use some popular varieties.
Avocado
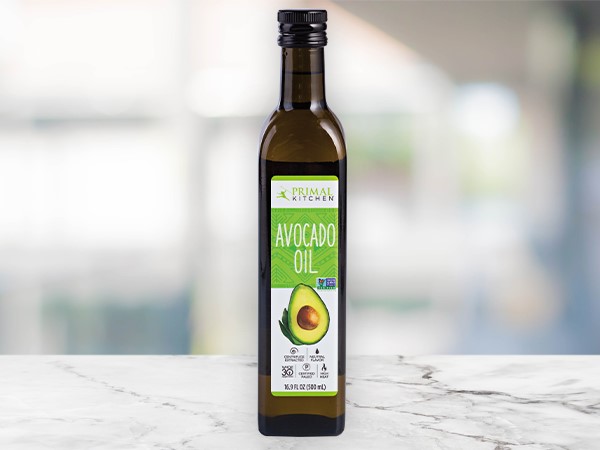

Flavor: Made from avocado, the trendy new fat, the oil has a slightly grassy and mild avocado flavor.
Best Uses: Great for frying and on salads, but also use for searing, grilling, baking, sauteing, and roasting.
Benefits: The highest smoke point of all plant-based cooking oils, it is also a good choice for the paleo diet. High in heart-healthy monosaturated fats and lower in saturated fat than many other oils.
Smoke Point: 520 degrees; very high.Hyvee Culinary Expert Tip
The smoke point of an oil is the temperature at which oil stops simmering and starts smoking and breaking down. Not only does it release harmful free radicals and chemicals at this stage, but it will also give the food an undesirable flavor. If you surpass the smoke point, the oil can start a grease fire.Sunflower
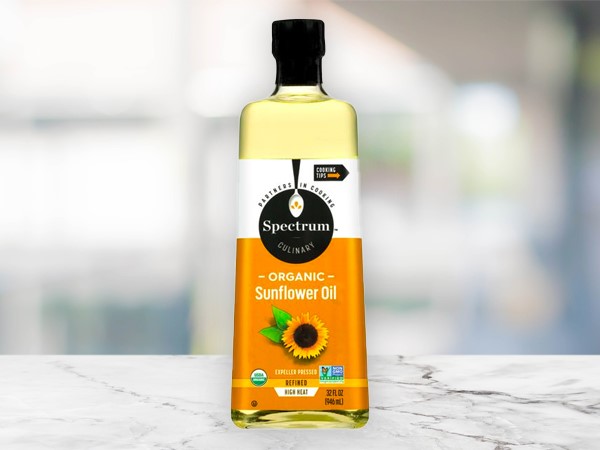

Flavor: Extracted from sunflower seeds, it bears a subtle flavor and can be used in place of any neutral vegetable oil.
Best Uses: The oil can be used for deep-frying, pan-frying, sauteing, roasting, and grilling
Benefits: Gaining popularity in the U.S., this oil has a high proportion of essential fatty acids that make it a good choice for heart health.
Smoke Point: 440 degrees; high.Canola
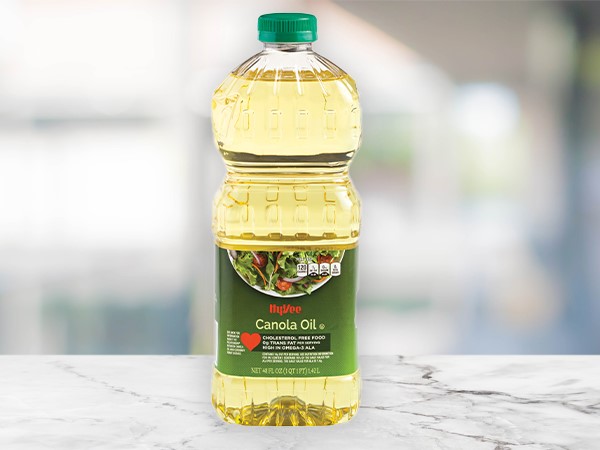

Flavor: Derived from rapeseed, a mustard relative; this oil has a neutral flavor making it a favorite among oils.
Best Uses: The versatile and popular oil can be used for frying, deep-frying, sauteing, stir-frying, grilling, and baking.
Benefits: One of the better-known oils, it is a healthy choice for consuming as it is low in saturated fat and has a high proportion of monosaturated fat.
Smoke Point: 401 degrees; high.Vegetable

Flavor: A blend of many different refined oils, its neutral flavor and lack of aroma make it great for various cooking purposes.
Best Uses: Can be used for many types of cooking, including high-heat, sauteing, and frying.
Benefits: An inexpensive choice, unhydrogenated vegetable oils are seen as healthy sources of fat.
Smoke Point: 400 degrees; medium-highGrapeseed

Flavor: Extracted from seeds of winemaking grapes, it is valued for its neutral, clean, and nearly flavorless taste.
Best Uses: One of the more versatile oils, use it for sauteing, frying, and searing. Or even try it in your baking and salad dressings.
Benefits: Good Source of vitamin E and antioxidants. Studies have found consuming grapeseed oil may reduce blood clotting and inflammation.
Smoke Point: 390 degrees; medium-highUnrefined Coconut

Flavor: Extracted from coconut meat, coconut oil has a strong coconut flavor.
Best Uses: Best for medium heat sauteing of meats and vegetables, especially Thai and Indian recipes. Also can be used in baking.
Benefits: Contains fatty acids that metabolize quickly for spurts of energy along with high levels of lauric acid, good for ketogenic diets.
Smoke Point: 350 degrees; lowExtra-Virgin Olive

Flavor: Depending on how the olives are pressed, flavor can range from spicy and peppery to slightly sweet.
Best Uses: A low smoke point isn't the best for cooking other than sauteing, but drizzle it over pasta dishes, sauces, or use it for salad dressings.
Benefits: Full of antioxidants, olive oil can help fight inflammation. Studies show consuming it may lower the risk of stroke, the fifth leading cause of death in the U.S.
Smoke Point: 320 degrees; low